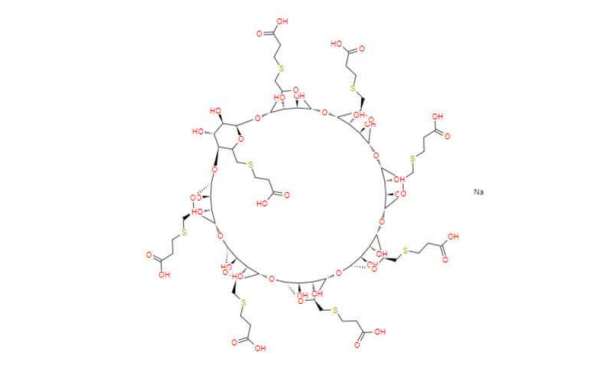
Mechanism of Action:
Sugammadex, a specially designed cyclodextrin molecule, works by:
Selective binding: It selectively binds to specific NMBAs, such as rocuronium and vecuronium, leaving other medications unaffected.
Encapsulation and removal: Once bound, sugammadex encases the NMBAs, effectively removing them from circulation and preventing them from further blocking the action of acetylcholine at the neuromuscular junction, the critical site for muscle activation.
Rapid reversal: This swift removal of NMBAs from circulation leads to a rapid reversal of the muscle relaxation effect, allowing patients to regain muscle function more quickly.
Advantages of Sugammadex Reversal
Compared to traditional methods that rely on the gradual breakdown of NMBAs in the body, sugammadex reversal offers several advantages:
- Faster recovery: Sugammadex significantly accelerates the return of muscle function, leading to faster patient recovery and shorter hospital stays. This can be particularly beneficial for procedures requiring prolonged NMBAs or for patients at higher risk of complications from prolonged immobility.
- Reduced risk of complications: Faster reversal of muscle weakness helps minimize the risk of postoperative complications like pneumonia, which can arise from prolonged inability to breathe independently.
- Improved patient comfort: By enabling quicker recovery of muscle function, sugammadex can significantly improve patient comfort and satisfaction following surgery or procedures.
Important Considerations
- Specificity: Sugammadex is not a universal reversal agent and is only effective for specific NMBAs. It's crucial to use the appropriate reversal agent based on the type of NMBA administered.
- Side effects: While generally well-tolerated, sugammadex can have its own side effects, although they are typically mild and manageable.
- Healthcare professional guidance: The decision to use sugammadex reversal should be made by a healthcare professional based on the individual patient's situation, the type of NMBA used, and potential risks and benefits.
In conclusion, sugammadex reversal represents a significant advancement in managing the effects of NMBAs. By offering faster recovery, reduced complication risks, and improved patient comfort, sugammadex plays a valuable role in enhancing patient outcomes and experiences following surgical procedures and interventions requiring neuromuscular blockade.